Good day and welcome again to TechCrunch’s China Roundup, a digest of latest occasions shaping the Chinese language tech panorama and what they imply to folks in the remainder of the world. This week, a post from Sequoia Capital sounding the alarm of the coronavirus’s impression on companies is reaching far corners of tech communities all over the world, together with China.
Many echo Sequoia’s statement that the businesses which can be the “most adaptable” are the likeliest to outlive. Others cling to the hope of “[turning] a difficult state of affairs into a possibility to set your self up for enduring success.”
Two weeks in the past I wrote about how the non-public sector and the federal government in China are working collectively to comprise the epidemic, bringing a short lived enhance to the expertise trade. This week I requested a lot of traders and founders which of those modifications will stand to final, and why.
B2B on the rise
The business-to-business (B2B) area was hardly ever a sizzling matter in China till on-line shopper companies grew to become comparatively saturated in latest occasions. And now, the COVID-19 epidemic has unexpectedly breathed life into the once-boring subject, which stretches from digital conferences, on-line training, digital healthcare, cybersecurity, telecommunications, logistics to sensible cities, evaluation from funding agency Yunqi Partners exhibits.
For one, there may be an apparent alternative for distant collaboration instruments as folks earn a living from home. Downloads of indigenous work apps like Dingtalk, WeChat Work, TikTok’s sister Lark in addition to America’s Zoom jumped exponentially amid the well being disaster. Whereas some argue that the growth is overblown and can dissipate as quickly as companies are again to regular, others counsel that the shift in conduct will endure.
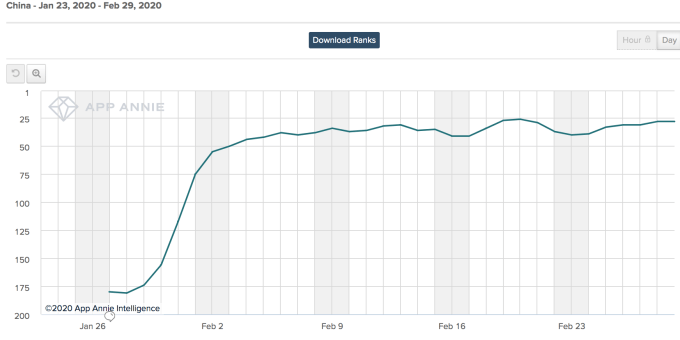
Like different work collaboration providers, Zoom soared in China amid the coronavirus outbreak, leaping from No. 180 in late January to No. 28 as of late February in general app installs. Data: App Annie
“Individuals are reluctant to vary as soon as they type a brand new behavior,” suggests Joe Chan, companion at Hong Kong-based Mindworks Ventures. The virus outbreak, he believes, has educated the Chinese language plenty to work remotely.
“Assembly in individual and thru Zoom each have their very own deserves, relying on the social norm. Some individuals are used to pondering that relationships should be established by means of face-to-face encounters, however those that don’t maintain that view may have fewer conferences. [The epidemic] presents an opportunity for a paradigm shift.”
However modifications are sluggish
Development in enterprise companies is perhaps much less seen than what China witnessed over the SARS epidemic that fueled web shopper verticals comparable to ecommerce. That’s as a result of software-as-a-services (SaaS), cloud computing, well being tech, logistics and different enterprise-facing providers are intangible for many shoppers.
“In comparison with modifications in shopper conduct, the adoption of recent applied sciences by enterprises occur at a slower tempo, so the impression of coronavirus on new-generation improvements [B2B] gained’t come as quickly and completely as what occurred throughout SARS,” contended Jake Xie, vp of funding at China Growth Capital.
Xie additional recommended that the alternatives offered by the outbreak are reserved for firms which were steadily investing within the subject, partially as a result of enterprise providers have an extended life cycle and require extra capital-intensive infrastructure. “Opportunists don’t stand an opportunity,” he concluded.
As for altering shopper conduct, such because the uptick in grocery supply utilization by seniors trapped indoors, the impression is perhaps short-lived. “The one profit that the epidemic brings to those apps is getting extra folks to strive their providers. However what number of of them will keep? The argument that individuals will preserve utilizing these apps over considerations of getting sick in offline markets is unsubstantiated. The energy of a enterprise lies in its means to resolve person issues in the long run, for instance, offering affordability and comfort,” recommended Derek Shen, chairman of Danke Condominium, the Chinese language co-living startup slated to list on NYSE.
Summoned by Beijing
The adjoining sector of enterprise providers — at-scale applied sciences tailor-made to energizing authorities features — has additionally seen traction over the course of the epidemic. Non-public corporations in China have teamed up with regional authorities to raised monitor folks’s actions, ramp up facial recognition capacities aimed toward a mask-wearing public, develop contact-free shopper expertise, amongst different measures.
Tech corporations touting providers to the federal government aren’t any stranger to criticisms regarding the lack of transparency in how person information is used. However the attraction to non-public corporations is large, not solely as a result of state contracts have a tendency to supply a gradual stream of long-term income, but additionally that sure public-facing initiatives might be billed as a achievement of company social tasks. Following the virus outbreak, Chinese language tech firms of all sizes hastened to supply contributions, with efforts starting from making financial donations to constructing instruments that preserve the general public knowledgeable.
On the flip aspect, the federal government additionally wants non-public assist in emergency administration. As outstanding Chinese language historian Luo Xin poignantly identified in podcast SurplusValue’s recent episode [1:00:00], a number of the best and efficient responses to the general public well being disaster got here not from the federal government however the non-public sector, whether or not it’s on-line retailer JD.com or logistics agency SF Specific delivering reduction provides to the epicenter of the outbreak.
That stated, Luo argued there are indicators that some native authorities’ tendency to centralize management is getting in the way in which of personal efforts. For instance, some authorities workplaces have stumbled of their makes an attempt to develop disaster administration techniques from scratch, overlooking a pool of available and confirmed infrastructure powered by the nation’s tech giants.